Validation of a Visual Prostate Symptom Score in Men With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in a Health Safety Net Hospital (PDF)
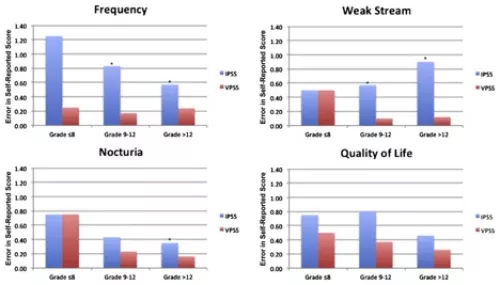
Objective: To evaluate the correlation between the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and the Visual Prostate Symptom Score (VPSS), a visual assessment of urinary stream, frequency, nocturia, and quality of life using pictograms, in a health safety net population.
Methods: Men presenting to San Francisco General Hospital with lower urinary tract symptoms completed the IPSS and the VPSS without and then with assistance. Statistical analysis was performed using the chi-square test, the Wilcoxon signed rank test, and the Spearman rank correlation.
Association of Patient Volume With Online Ratings of California Urologists (PDF)
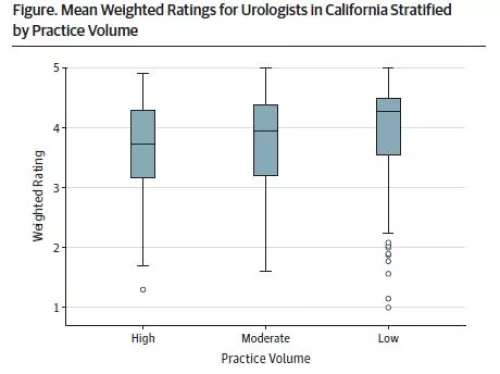
Objective: This study evaluates Medicare billing data to examine whether urologists with higher patient volume have lower online ratings from patients.
Background: Online reviews are an increasingly popular tool for patients to evaluate and choose physicians.1 Although the accuracy, utility, and meaning of online reviews are debated by physicians, the patient perspective is a valued component of the physician-patient relationship and is likely to increase in importance.2,3 Reliable online reviews provide guidance for health care consumers as well as feedback to physicians. Online reviews are influenced by many factors, including patient wait times; however, little else is known about physician practice patterns and their effect on reviews.4 We evaluated Medicare billing data and online reviews of urologists in California, with the hypothesis that urologists with higher-volume practices would have lower patient ratings, potentially owing to shorter physician-patient interactions and increased wait times.
Use of an Online Crowdfunding Platform for Unmet Financial Obligations in Cancer Care (PDF)
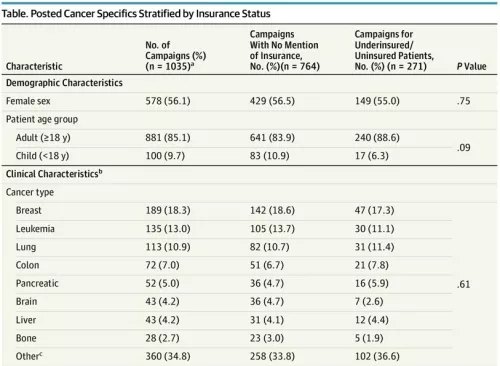
Background: Technologic innovations, expensive new therapies, and improved access to treatment have all contributed to the rising costs of oncologic care in the United States.1 The financial consequences for patients and their families are substantial. Patients with cancer often borrow money, avoid leisure activities, decrease food spending, sell possessions, go into debt, and/or declare bankruptcy,2 and they are at greater risk for disability or unemployment.3 These consequences are particularly great for patients who are underinsured or uninsured. Recently, online crowdfunding platforms are being increasingly used to supplement insurance and defray expenses, even for experimental and unproven treatments.4 We sought to characterize the use of crowdfunding to support oncology care needs, including any association between insurance status and other characteristics.
Methods: We identified the top 20 most prevalent cancers in the United States using data from the National Cancer Institute. Each cancer and US state was queried on the GoFundMe platform (www.gofundme.com) for 1000 individual searches (50 states × 20 top cancers = 1000 batches of searches).
Resident-Driven Holistic Lean Daily Management System to Enhance Care Experience at a Safety Net Hospital (request PDF)
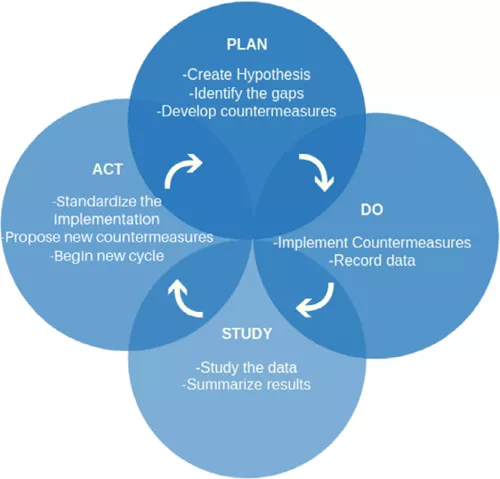
Objective: To describe the use of Lean in urology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General, a community safety-net and trauma hospital that serves as a major teaching site for the University of California San Francisco.
Methods: We examined our process improvement activities from 2016 to 2018. Our Lean Daily Management System (DMS) includes a 15-minute team huddle ("urology Lean work") of service residents, faculty, clinic and operating room nursing staff, and anesthesia liaisons. Our DMS also includes a 5-minute preoperative huddle. Besides team-building, urology Lean work surfaces logistics, safety or equipment improvement ideas, and ensures progress and completion of initiated projects.
Results: Over a 2-year period we developed and completed 67 projects. Projects impacted the outpatient setting (57%), followed by the operating room (22%), the Urology service (12%), and inpatient setting (9%). We completed projects in the following domains: safety (26%), quality (22%), care experience (21%), workforce care and development (13%), equity (11%), and financial stewardship (7%)...
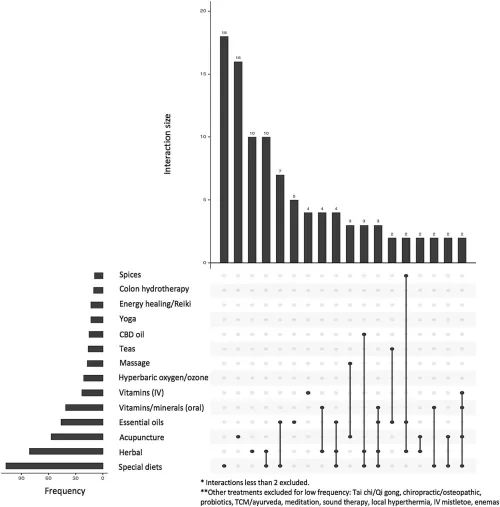
Use of GoFundMe ® to crowdfund complementary and alternative medicine treatments for cancer (PDF)
Purpose: Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) use is common amongst cancer patients. However, there is growing concern about its safety and efficacy. Online crowdfunding campaigns represent a unique avenue to understand the cancer patient's perspective for using CAM or declining conventional cancer therapy (CCT).
Methods: Five hundred GoFundMe campaigns from 2012 to 2019 detailing financial need for cancer treatment were randomly selected and reviewed for endorsement of CAM use, reasons for using CAM, and reasons for declining CCT. Descriptive statistics were used to compare patient and campaign characteristics between 250 CAM users and 250 non-CAM users.
Results: Compared to non-CAM users, CAM users were more likely to be female (70% vs. 54%, p < 0.01), to report more stage IV cancer (54% vs. 12%, p < 0.01), and to have a history of delayed, missed, or misdiagnosis (10% vs. 4%, p < 0.01). Reasons for using CAM include endorsing curative/therapeutic effects 212 (85%), pain/stress reduction 137 (55%), and dissatisfaction with current or past medical treatment options 105 (42%). 87 (35%) CAM users that declined CCT reported that they wanted to try to fight off cancer using CAM first 57 (61%), that CCT was too "toxic" to the body 39 (42%), and cancer was already too advanced, so that CCT would be futile or too aggressive 25 (27%).
Dedicated Residency Research Time and Its Relationship to Urologic Career Academic Success (request PDF)
Objective: To explore the relationship between research time during urologic training and career academic success.
Methods: We included urologists graduating residency between 2002 and 2008 from 36 programs affiliated with a top 50 hospital for urology as ranked by the United States News and World Report, and collected research time during residency, fellowship training, current appointment (private practice, assistant professor, associate professor, professor, chair), national institutes of health (NIH) grant accrual, NIH R01 grant accrual, and current H-index in Scopus database. Publication output during and after residency was identified through the PubMed database.
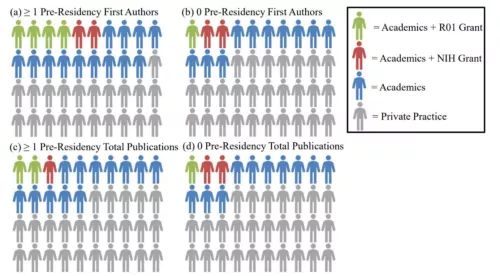
Predictive Factor of Pre-Residency Publication on Career Academic Achievement in Urologists
Introduction: Publications at any point in training can impact future academic interest and achievement. Implications of publishing scholarly work prior to residency on accomplishments during and after residency are under-studied.
Methods: We obtained publication output before, during, and after residency for urologists graduating between 2002 and 2008 from the 36 training programs affiliated with a top 50 urology hospital nationwide. Additional collected information included fellowship training, current appointment, total and R01 National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants, and h-index. We compared urologists’ pre-residency scholarship with residency and career achievements.
Playground Equipment-related Genital Injuries in Children: An Analysis of United States Emergency Departments Visits, 2010-2019
Objective: To evaluate the demographics, epidemiology, and common mechanisms associated with playground equipment-related genital injuries in children.
Methods: We examined the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System database to obtain playground-related genital injuries sustained in children ≤17 years from 2010 to 2019. Demographics of the patients and injury characteristics were analyzed using sample weights to produce national estimates.
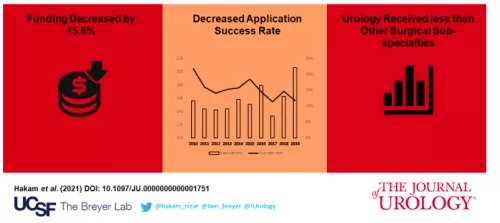
Contemporary Trends and End-Results of National Institutes of Health Grant Funding to Departments of Urology in the United States: A 10-year Analysis
Purpose: We explored the patterns and distribution of National Institutes of Health grant funding for urological research in the United States.
Materials and methods: The National Institutes of Health RePORTER database was queried for all grants awarded to urology departments between 2010 and 2019. Information regarding the value of the grant, funded institution, successful publication of the research, and the category of urological subspecialty were collected. Data on principal investigators were extracted from publicly available information.