Exercise Improves Self-Reported Sexual Function Among Physically Active Adults (PDF)
Background: Sexual dysfunction is common among adults and takes a toll on quality of life for bothmen andwomen.
Aim: To determine whether higher levels of weekly cardiovascular exercise are protective against self-reported sexual dysfunction among men and women.
Methods: We conducted an international online, cross-sectional survey of physically active men and women between April and December 2016, assessing exercise activity categorized into sextiles of weekly metabolic equivalent-hours. Odds ratios (ORs) of sexual dysfunction for each activity sextile compared with the lowest sextile were calculated using multivariable logistic regression, controlling for age, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, tobacco/alcohol use, sport, and marital status.
See more
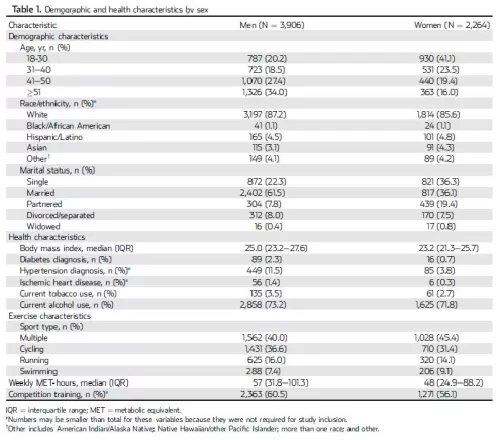
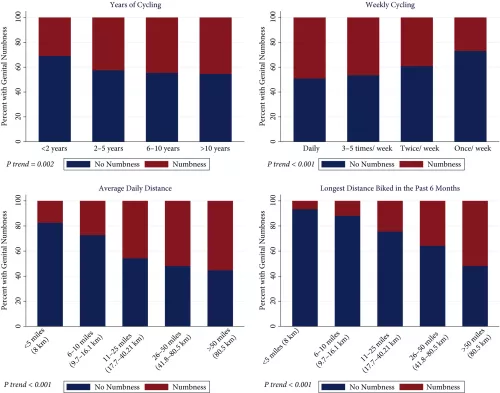
The Association of Bicycle-related Genital Numbness and Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) Score (PDF)
Objective: To assess the association of genital numbness and erectile dysfunction in male cyclists.
Subjects and Methods: Cyclists were recruited through Facebook advertisements and outreach to sporting clubs. This is a secondary analysis of a larger epidemiological population-based study that examined sexual and urinary wellness in athletes. We queried cycling habits and erectile function using Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM).
Results: A total of 2 774 male cyclists were included in the analysis. Amongst cyclists, there was a statistically significant increase in the trend of genital numbness presence with more years of cycling (P = 0.002), more frequent weekly cycling (P < 0.001), and longer cycling distance at each ride (P < 0.001). Less frequent use of padded shorts (odds ratio [OR] 0.14, P < 0.001) and lower handlebar (OR 0.49, P < 0.001) were associated with numbness, but body mass index (BMI) (OR 1.1, P = 0.33) and age (OR 1.2, P = 0.15) were not.
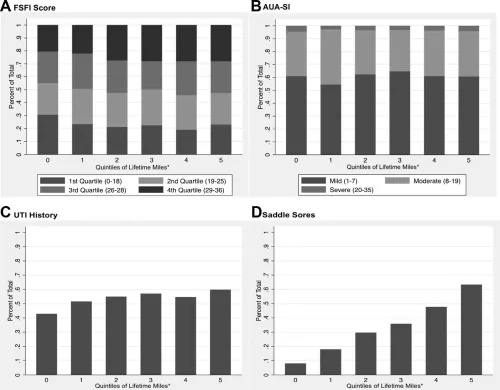
Cycling and Female Sexual and Urinary Function: Results From a Large, Multinational, Cross-Sectional Study (PDF)
Background: Bicycle riding has become an increasingly popular mode of transportation and exercise, especially among women, and previous studies have demonstrated a relationship between cycling and sexual dysfunction, albeit using non-validated questionnaires.
Aim: We aimed to explore the relationship between cycling and sexual and urinary dysfunction.
Methods: Cyclists were recruited to complete a survey through Facebook advertisements and outreach to sporting clubs across 5 English-speaking countries. Swimmers and runners were recruited as a comparison group.
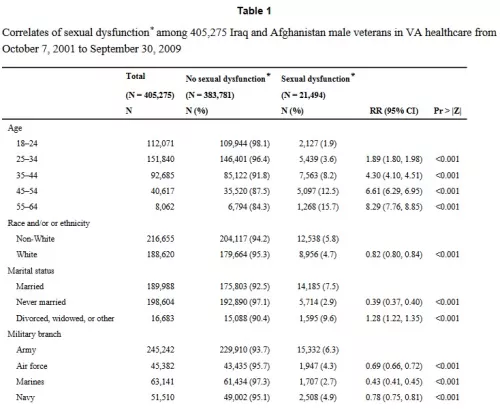
Sexual Dysfunction in Male Iraq and Afghanistan War Veterans: Association with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Other Combat-Related Mental Health Disorders: A Population-Based Cohort Study (PDF)
Aims: We sought to determine the prevalence and correlates of sexual dysfunction among male Iraq and Afghanistan veterans.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of 405,275 male Iraq and Afghanistanveterans who were new users of U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs healthcare from October 7,2001 to September 30, 2009 and had 2-year follow-up
Main Outcome Measures: We determined the independent association of mental healthdiagnoses and sexual dysfunction after adjusting for sociodemographic and military servicecharacteristics, comorbidities, and medications.
Qualitative analysis of Amazon customer reviews of penile clamps for male urinary incontinence (request PDF)
Methods: We collected Amazon reviews of all penile clamps marketed for male urinary incontinence from November 2011 to January 2020 and qualitatively assessed the overall sentiment towards penile clamps, key praises and key complaints. Covariates such as designated Amazon star rating were further explored for association with coding patterns.
Evaluating the primary use, strengths and weaknesses of pelvic floor muscle training devices available online (PDF)
Aims: Treatment for urinary incontinence (UI) includes pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT). There is limited data appraising the characteristics of PFMT devices. We aimed to ascertain the primary use, strengths and weaknesses of PFMT devices available online, through evaluation of consumer reviews.
Methods: We performed an analysis of PFMT devices on Amazon.com. Four key device categories were recognized. Reviews from the five most frequently-reviewed products per category were analyzed (n = 20). W characterized device use, strengths and weaknesses using thematic analysis.
Results: We evaluated 2574 PFMT device reviews including 1168 vibrating Kegel balls, 750 non-vibrating Kegel balls, 411 pelvic floor or thigh exercisers, and 245 electric probes. Non-vibrating Kegel balls were rated highest (4.6/5 stars), followed by vibrating Kegel balls, electric probes and pelvic floor or thigh exercisers (4.4/5, 4.1/5, and 3.8/5 stars, respectively). Most reviews were positive (77%) or negative (16%) with few neutral (7%). While all were marketed to treat UI, most reviews did not mention the intended use...